
For generations, cannabis cultivators have been attuned to the delicate nuances of their crops. Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD) stands as a critical metric, offering insights into the hydration environment of plants.
Today, with the augmentation of IoT devices, understanding and controlling VPD has transitioned from an art to a precision science.
Why Monitor VPD?
VPD influences the rate at which plants uptake water and nutrients. It provides a snapshot of the plant's hydration environment by gauging the difference in vapor pressure between the plant's leaf and its surroundings. A favorable VPD encourages optimal cellular processes, efficient nutrient absorption, and healthy growth rates, especially for cannabis plants.
An imbalanced VPD can stress the plant, leading to slow growth, wilting or even the onset of diseases. For cannabis, improper VPD levels can affect the yield and potency of the buds, making this parameter crucial for cultivators seeking a premium flower.
What Are We Monitoring?
- Leaf & Ambient Vapor Pressure: By comparing the vapor pressure inside the leaf to that of the surrounding environment, VPD can be accurately determined.
- Example Value: A VPD of 0.8-1.2 kPa (kilopascal) is often optimal for the flowering stage of cannabis.
- How This Telemetry is Represented: VPD readings are usually depicted in graphical formats on IoT dashboards, providing real-time trends and historical data analysis. This visual representation aids cultivators in spotting patterns or irregularities quickly.
 VPD is often not the only measure you want to capture. Stomatal conductance, leaf area and light intensity all play a critical role in understanding how to manage your VPD.Shawn Deggans
VPD is often not the only measure you want to capture. Stomatal conductance, leaf area and light intensity all play a critical role in understanding how to manage your VPD.Shawn Deggans
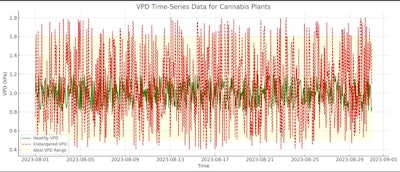
Time-Series Analysis and Display
As visualized in the chart:
- The green line represents the VPD values for a healthy cannabis plant, fluctuating within the ideal range.
- The red dashed line indicates the VPD values for a potentially endangered cannabis plant, showing values both within and outside the ideal range.
- The yellow-shaded region demarcates the consistent VPD range for cannabis plants.
Devices for Monitoring VPD
- VPD Sensors: These specialized sensors gauge the difference in vapor pressure, offering instant readings. Their quick response time and precision make them invaluable for modern cannabis cultivation.
- Porometer: A porometer measures stomatal conductance, indicating how open or closed the stomata are on a leaf's surface, thereby providing insights into the transpiration rate.
- Integrated Climate Systems: A more holistic approach, these systems not only measure VPD but also other critical metrics like temperature and humidity. Their interconnected nature offers a comprehensive view of the cultivation environment.
- Remote IoT Monitoring Platforms: With advancements in IoT, cultivators can now get real-time VPD data on their smartphones or computers. These platforms can alert growers to any sudden changes, enabling swift interventions.
Interpreting Data
- Understanding the Ideal Range: For cannabis, the optimal VPD range varies with the growth stage. Seedlings prefer a VPD of 0.4-0.7 kPa, while mature plants during flowering find 0.8-1.2 kPa more suitable.
- Recognizing Outliers: A sudden spike or drop in VPD values may indicate issues like equipment failure or environmental disturbances. Rapid detection can lead to timely solutions, minimizing potential damage.
Testing and Calibration
- The Importance of Accuracy: Given the sensitive nature of cannabis to VPD levels, ensuring that monitoring equipment is accurate is important.
- Testing Procedures: Regularly cross-referencing VPD readings from IoT devices with trusted manual instruments can ascertain their accuracy.
- Calibration Steps: Devices often come with calibration kits and guidelines. Following manufacturer instructions or seeking expert assistance guarantees that measurements remain reliable.
Using Data for Cultivation Decisions
- Adjusting Humidity and Temperature: These are the two primary factors influencing VPD. By adjusting them based on IoT data, cultivators can maintain an ideal VPD.
- Incorporating Other Data: While VPD is vital, it's essential to consider it alongside other metrics like nutrient levels and lighting. A holistic approach ensures balanced growth.
- Long-term Planning: Over time, consistently tracking VPD can inform decisions about seasonal changes, equipment upgrades, or modifications in cultivation techniques.
By harnessing the power of IoT and scientific instruments, cultivators can transform insights into actions, ensuring that their crops thrive and the end product is premium.
This article is part three of an exclusive new series that will guide you through the essence of each of the fourteen pillars of plant care, focusing on indoor growth and revealing the nuances of how IoT can be a game-changer for cultivators.
Shawn Deggans owns Green Nanny, an IoT, AI and data consulting company focused on helping growers spend more time in the garden and less time struggling with technology.























