
Nutrition and fertilization are foundational in the cultivation of indoor medical cannabis. Proper nutrient provision ensures plants thrive, maximizing yield and potency. In today's digital age, IoT devices serve as the bridge between traditional practices and cutting-edge cultivation, providing real-time insights into the plant's nutritional needs.
Nutrition fuels every cellular process in the cannabis plant. It dictates growth rate, influences cannabinoid production, and affects overall plant health.
Over-fertilization can lead to nutrient burn, while insufficient nutrition can stunt growth, weaken immunity, and reduce yield. Balancing nutrient supply is required to avoid these pitfalls.
What Are We Monitoring?
Telemetry Types:
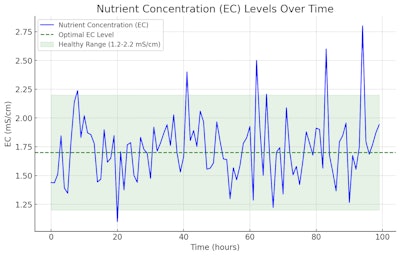
- Nutrient Parts Per Million (PPM): Measures the concentration of nutrients in a solution, providing insights into the nutrient strength.
- Example Value: 900 PPM.
- Nutrient Ratios: Specific ratios of key nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium which are vital for different growth stages.
- Example Value: N:P:K = 3:1:2.
- How This Telemetry is Represented: Nutrient data is typically plotted over time in bar or line graphs, indicating how nutrient concentrations change throughout the growth cycle.
Devices for Monitoring Nutrition and Fertilization
- Digital PPM Meters: Provide real-time data on nutrient concentration, helping cultivators adjust feedings on the fly.
- IoT-Connected Nutrient Sensors: These devices continuously monitor nutrient levels, sending alerts for any imbalances or required adjustments.
- Automated Dosing Systems: Integrated with IoT, these systems auto-adjust nutrient concentrations in water reservoirs based on real-time data.
Interpreting Data
- Understanding the Ideal Range: Depending on the growth stage, cannabis plants require different PPM ranges. For instance, vegetative stages might range from 300-800 PPM, while flowering can go up to 500-1000 PPM.
- Recognizing Outliers: A sudden drop in PPM might indicate a nutrient lockout, while a spike could mean potential over-fertilization.
Testing & Calibration
- The Importance of Accuracy: Precision in nutrient delivery ensures plants get exactly what they need, optimizing growth and yield.
- Testing Procedures: Cross-reference readings with lab-grade equipment to ensure accuracy.
- Calibration Steps: Regularly recalibrate PPM meters using standard calibration solutions to ensure they provide accurate readings.
Using Data for Cultivation Decisions
- Adjusting Nutrient Solutions: Depending on the growth stage and current PPM readings, cultivators might increase or decrease nutrient strength.
- Incorporating Other Data: Consider nutrition data alongside factors like water quality and pH. Their combined insights dictate overall feeding strategies.
- Long-term Planning: Consistent nutrient data helps refine future feeding schedules, optimizing nutrient delivery for each growth cycle.
Monitoring nutrition and fertilization is not just beneficial—it's crucial for the success of indoor medical cannabis cultivation. With the advent of IoT devices, cultivators now have a window into the very cellular processes of their plants.
By embracing this technology, cultivators can ensure that their plants receive the perfect balance of nutrients, leading to healthier plants, higher yields, and superior quality flower.
This article is part seven of an exclusive new series that will guide you through the essence of each of the fourteen pillars of plant care, focusing on indoor growth and revealing the nuances of how IoT can be a game-changer for cultivators.
Shawn Deggans owns Green Nanny, an IoT, AI and data consulting company focused on helping growers spend more time in the garden and less time struggling with technology.























