
Oxygen plays a crucial role in the health of plants, especially within their root systems. In our technologically advanced era, Internet of Things (IoT) devices have become indispensable in ensuring plants receive the right amount of oxygen for optimal growth.
Oxygen supports the respiration process in plant cells, particularly in the roots. Proper oxygenation ensures efficient nutrient uptake and energy production.
Hypoxia, as a result of insufficient oxygen, can hinder root growth, reduce nutrient absorption and raise susceptibility to diseases like root rot.
What Are We Monitoring?
Telemetry Types
- Oxygen Concentration in the Growing Medium: Measures the oxygen percentage in the soil or hydroponic solution.
- Example Value: 8% oxygen concentration.
- Root Zone Respiration Rate: Assesses the rate at which plant roots consume oxygen.
- Example Value: 5 mL O2 per gram of root per hour.
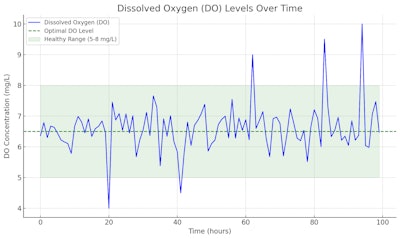
- Dissolved Oxygen (DO) Concentration: Reflects oxygen saturation in hydroponic solutions or water reservoirs.
- Example Value: 6.5 mg/L DO concentration.
- How This Telemetry is Represented: Data is typically visualized through graphs, showcasing concentration levels or consumption rates over time.
Devices for Monitoring Oxygen and Oxygenation
- Oxygen Electrochemical Sensors (galvanic): These sensors provide real-time data on oxygen concentration in growing mediums.
- IoT-Connected Dissolved Oxygen Meters: Useful for hydroponics, they measure dissolved oxygen in water solutions.
- Root Respirometers: These evaluate root oxygen consumption, providing insights into root health. Note: these are primarily used in labs and are not IoT devices.
Interpreting Data
- Understanding the Ideal Range: For many plants, including cannabis, a dissolved oxygen range of 5-8 mg/L is optimal. Soil-grown plants benefit from well-aerated soil.
- Recognizing Outliers: Sharp changes in oxygen levels can indicate problems such as overwatering or root diseases.
Using Data for Cultivation Decisions
- Adjusting Aeration Techniques: Oxygen data can inform the introduction of air stones in hydroponic tanks or the use of soil aeration methods.
- Incorporating Other Data: Oxygenation should be considered alongside metrics like moisture levels for a comprehensive cultivation approach.
- Long-term Planning: Data on oxygenation can guide decisions on growing medium choices and root health strategies.
Monitoring oxygen is essential for nurturing healthy plants. By leveraging IoT devices and scientific instruments, cultivators can gain unparalleled insights into their plants' oxygen needs, combining traditional knowledge with cutting-edge technology for optimal results.
This article is part twelve of an exclusive new series that will guide you through the essence of each of the fourteen pillars of plant care, focusing on indoor growth and revealing the nuances of how IoT can be a game-changer for cultivators.
Shawn Deggans owns Green Nanny, an IoT, AI and data consulting company focused on helping growers spend more time in the garden and less time struggling with technology.























